For example, CO₂ is decomposed semipermanently and continuously converted into raw materials through exposure to sunlight alone.
This is the Daicel nanodiamond solution.
Scroll
Ultrasmall diamonds continuously create new solutions that transform the future.
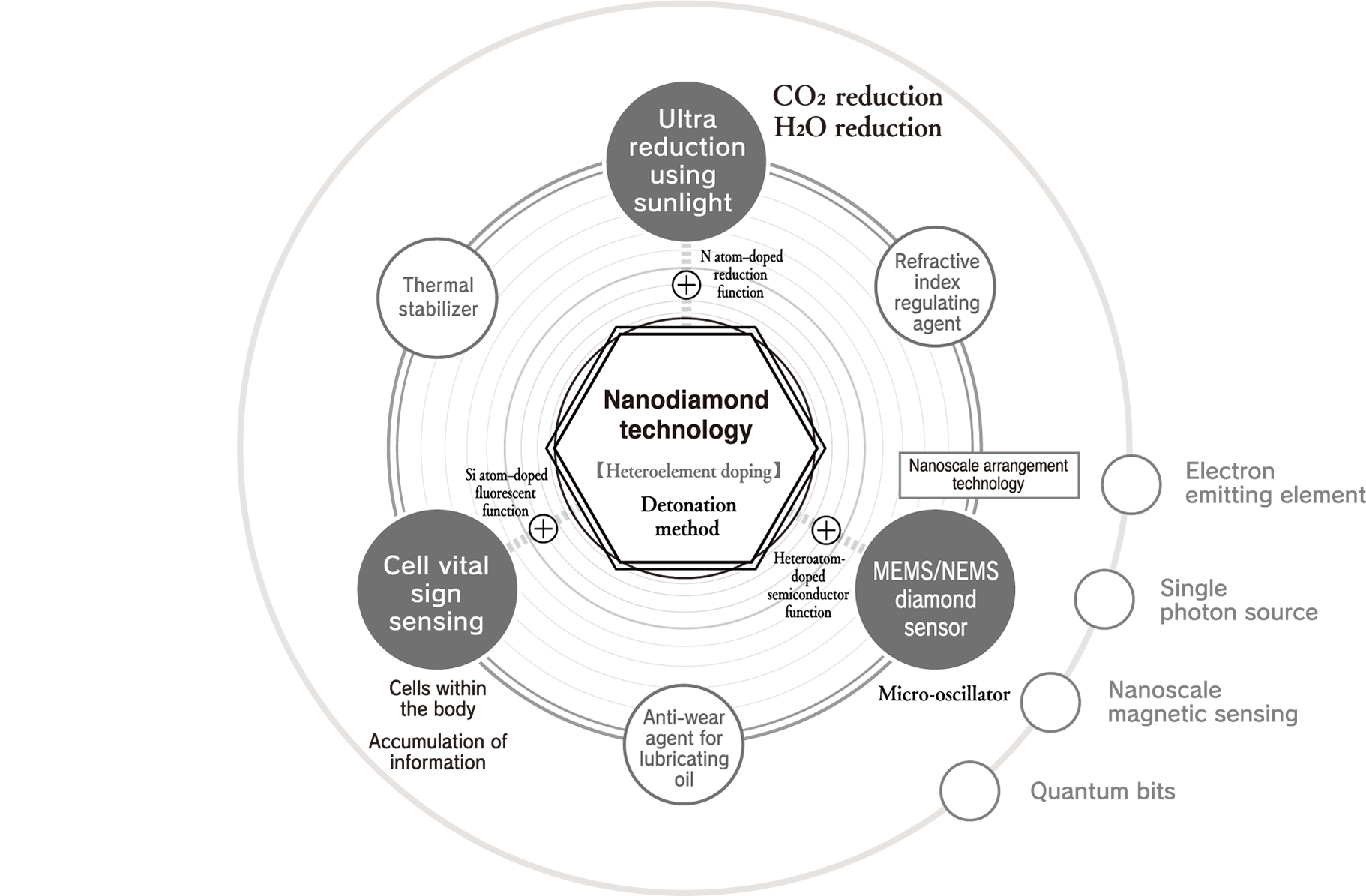
An example of this is sunlight super-reduction. CO₂ is continuously decomposed semipermanently with sunlight alone and converted into raw materials. Another example is cell vital sign sensing. Ultrasmall diamonds with a fluorescent function are introduced into human cells, and the condition of cells is sensed by detecting light emission from within the body. We also have the MEMS/NEMS diamond sensor. Nanodiamond particles with a semiconductor function are precisely arranged on a substrate at nanoscale to create a previously unheard of sensor with ultra-high sensitivity. These kinds of nanodiamond solutions that will change the future are continuously realized through Daicel’s nanodiamond technology, our unique nanodiamond generation technology in which different elements are doped into ultrasmall diamond particles by the detonation method.
Daicel’s nanodiamond solutions
Our nanodiamond technology is unique technology that evolves nanodiamonds.
The production of high-purity nanodiamonds is realized through Daicel’s unique chemical technology and “One Time Energy.”* They generate an ultra-extreme environment with a high temperature of 3,500 kelvin or more and a high pressure of 25 GPa or more in 1 ms or less with the detonation method and dope heteroelements into nanodiamonds in that instant to express various high functions. Only this unique nanodiamond technology can realize the production of highly functional nanodiamonds with overwhelming productivity.
Characteristics of nanodiamonds
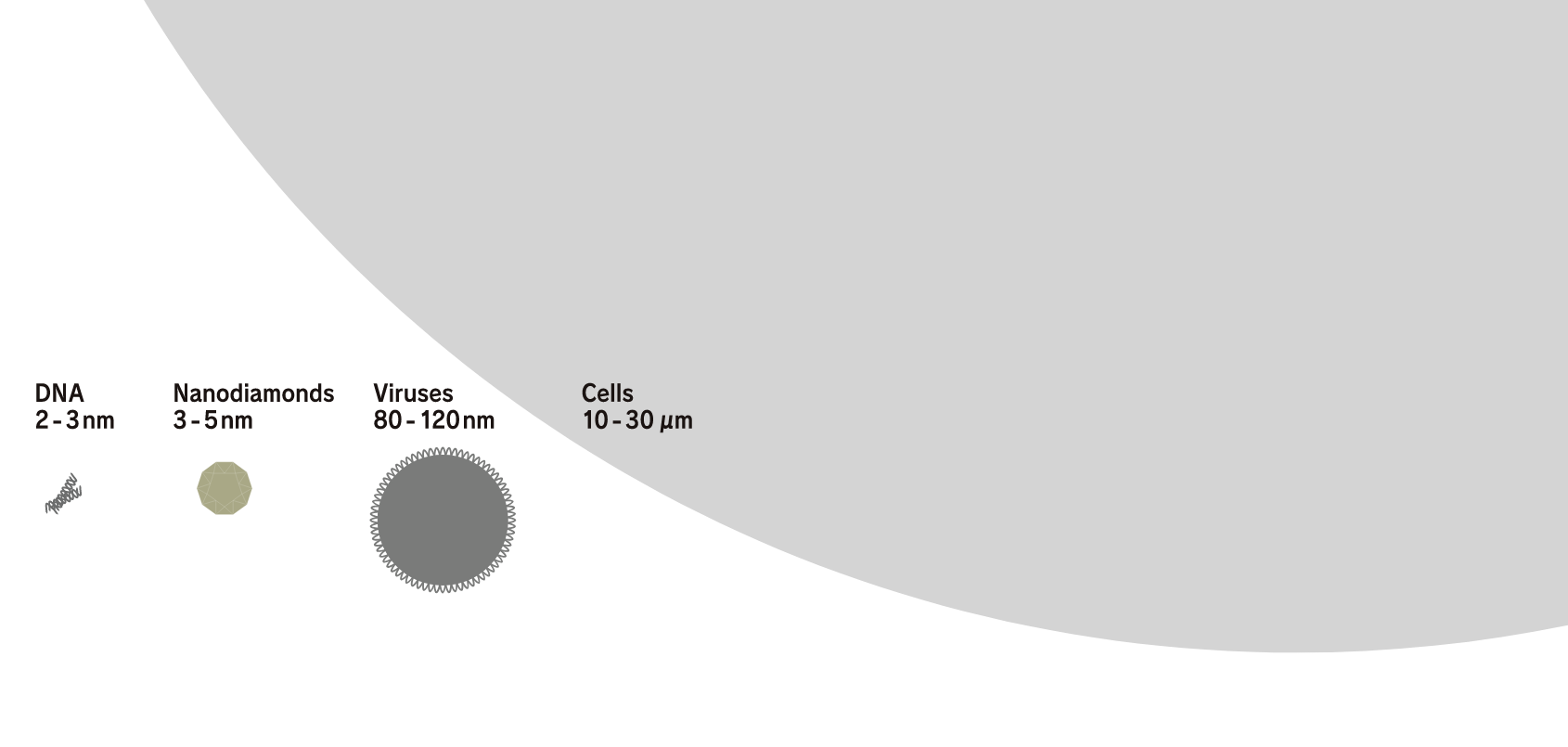
Their overwhelmingly small sizes and numbers produce a variety of new solutions.
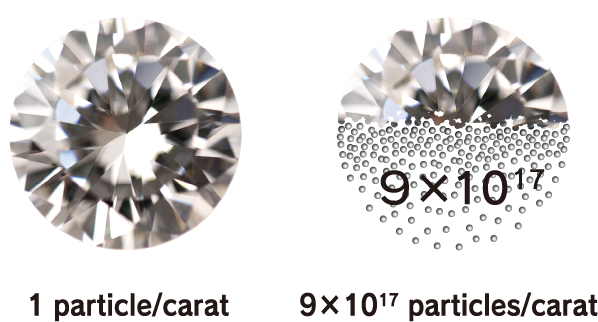
Nanodiamonds directly inherit the characteristics of large diamonds. For example, large diamonds are the hardest material on earth, have a thermal conductivity higher than any metal but do not conduct electricity, have both a high refractive index and high Abbe number, are very stable chemically, and do not react to any acids or alkalis, which makes them unique materials. Such characteristics are their most well-known industrial properties. In addition to these characteristics, nanodiamonds also have a feature that emerges due to their small size. Specifically, this is an overwhelming number of particles. For example, the number of particles in 1 carat is as many as 9 × 10 17 . If the number of particles is the key to a function, such as when nanodiamonds are compounded with other materials, this enormous number of particles is advantageous. In addition, in applications where the nanodiamond surface functions at the contact surface with other material, the function can be maximized when they are dispersed well.
Number of particles per carat: 9 × 10 17
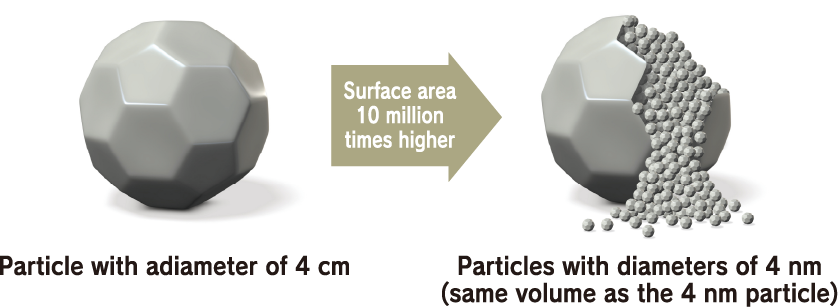
Surface area, the key to exerting function: 10 million times higher
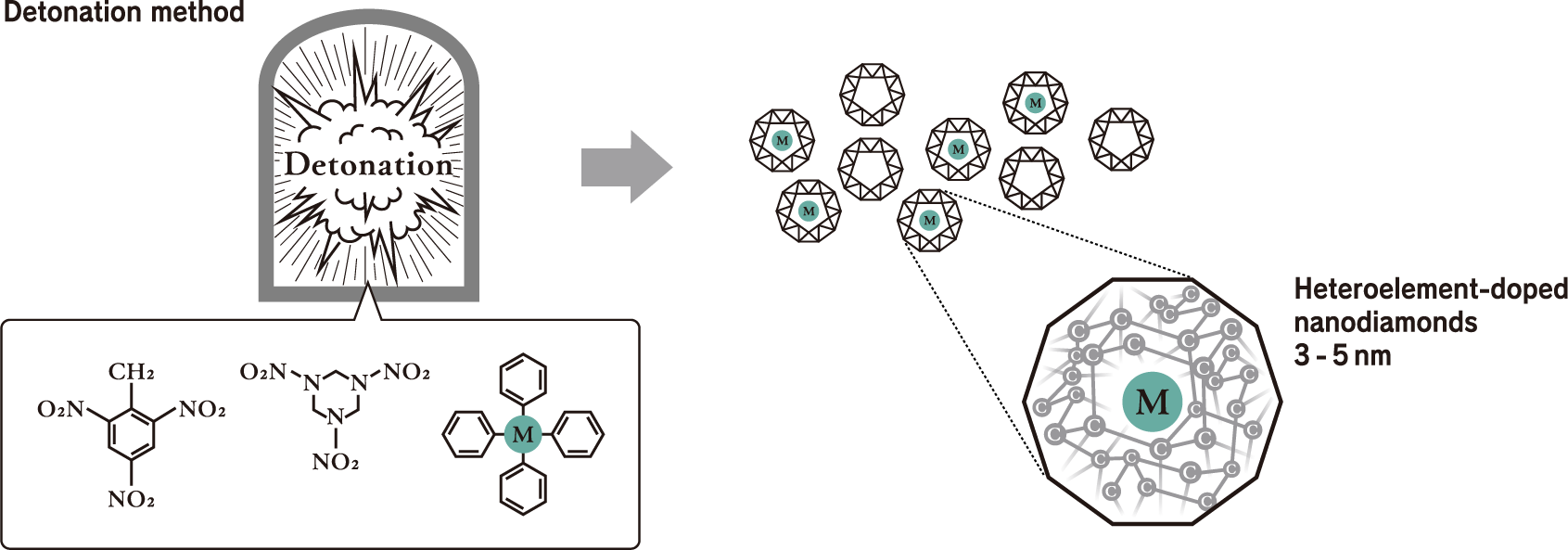
Mechanism for doping heteroelements into nanodiamonds
This is accomplished with nanodiamond technology produced by heteroelement doping via the detonation method, which can only be realized by Daicel. Heteroelement doping is a technology in which heteroelements such as silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge) are doped into nanodiamonds composed of only carbon atoms (C). As shown in the drawings below, the heteroelement (M) to be doped is mixed with two kinds of explosives, TNT and RDX. The materials to be mixed not only contain the elements you wish to incorporate into the nanodiamonds but also have optimal molecular structures so that they can be efficiently incorporated into the nanodiamonds in the detonation environment.